
Source: Unsplash/Alexander Grey
What distinguishes a company that makes “good” chocolate (chocolate untainted by child labour, modern slavery, deforestation and the overuse of agrichemicals) from one that merely makes chocolate?
Our annual Chocolate Scorecard investigation, which is a collaboration between Be Slavery Free, Macquarie University, The University of Wollongong and the Open University, suggests it might be a mission that goes beyond making food and profit.
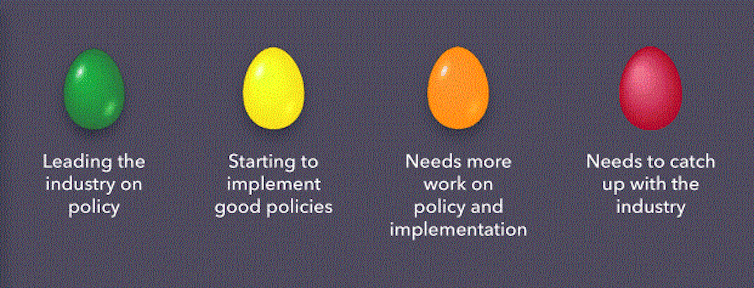
‘Good eggs’ trumpet ambition
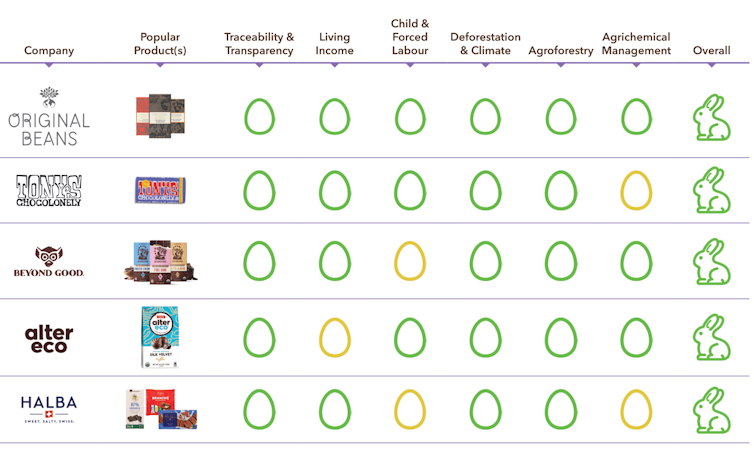
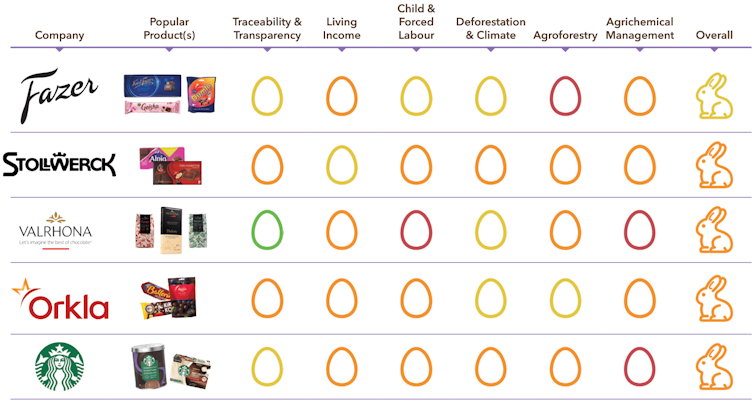
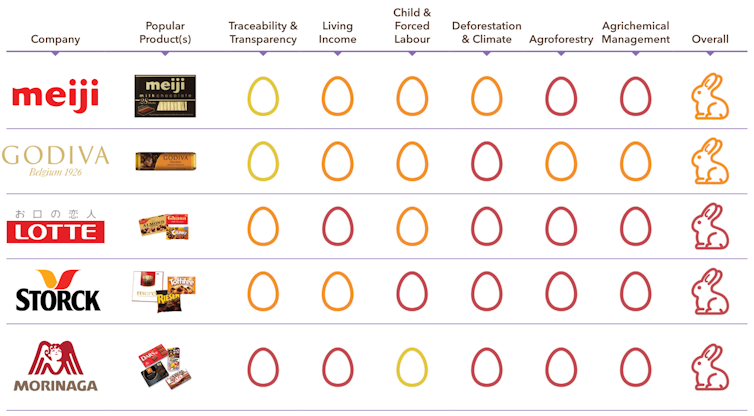
Only five of the 38 leading global chocolate makers we assessed received our green “good egg” award for exemplary practices.

They are the Netherlands-based Orignal Beans and Tony’s Chocolonely, Madagascar’s Beyond Good, US-based Alter Eco, and Switzerland’s HALBA.
Original Beans are at the forefront of Europe’s artisan chocolate revolution. Its mission statement includes the words “regenerate what you consume”. Its website asks its customers to “heal the future, don’t steal it”.
Tony’s Chocolonely has as its mission to make slave-free chocolate and turn all chocolate slave-free.
It says 60% of the world’s cocoa comes from 2.5 million farms in West Africa that are placed under the kind of pricing pressure that leads to child labour and modern slavery. The average cocoa farmer earns less than US$1.20 per day, and women cocoa farmers are thought to earn around 50 cents per day.
‘Broken eggs’ say little
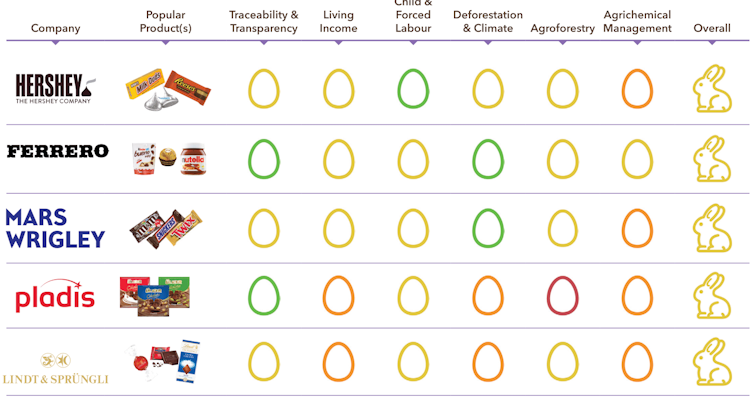
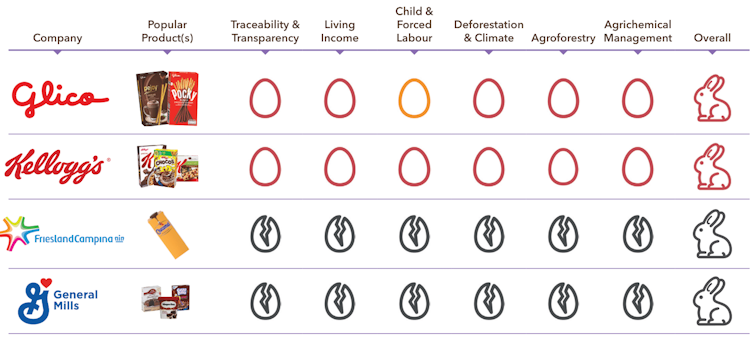
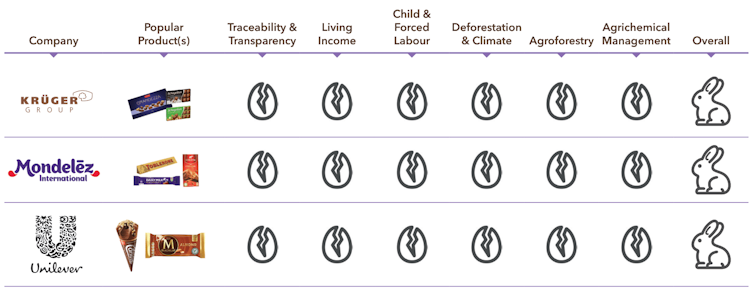
At the other end of the scale, firms such as Unilever (which makes Magnum icecreams) and Mondēlez (which makes Cadbury) were awarded “broken eggs” for not engaging with the survey.
Mondēlez describes its mission as going “the extra mile to lead the future of snacking around the world”, rather than tackling environmental or social concerns.
It’s a long way from Cadbury’s original mission. Founder John Cadbury was a Quaker “driven by a passion for social reform” who helped found the forerunner to the Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals and planned a “model village” for his workers including schools, shops, parks and childcare.
In 2022, Britain’s Channel 4 broadcast undercover footage from Ghana purporting to show children as young as 10 barefoot, wearing shorts and T-shirts, using machetes to harvest cocoa pods and sharpened sticks to extract beans that were eventually used in Cadbury chocolate.
Mondelēz said it was deeply concerned. It explicitly prohibited child labour and had been making significant efforts to improve the protection of children in the communities where it sourced cocoa, including Ghana.
If such efforts are afoot, Chocolate Scorecard would like to hear about them.
‘Rotten eggs’ can improve
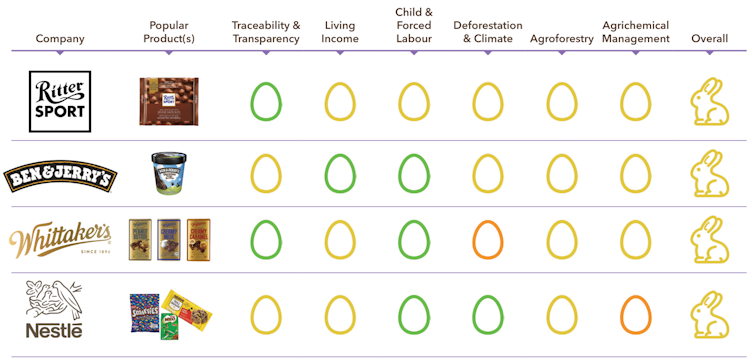
Among those companies that did respond, there are signs of improvement. In 2020, Godiva received a “rotten egg” award for “failing to take responsibility for the conditions with which its chocolates are made despite making huge profits off its chocolate”.
Godvia now says it is dedicated to “a sustainable and thriving cocoa industry where farmers prosper, communities are empowered, human rights are respected, and the environment is conserved”.
It has earned an “orange” rating, demonstrating that progress is achievable.
Similarly, Sücden — a previous red “rotten egg” — improved to yellow in this year’s scorecard.
Nestlé’s inclusion in this year’s top ten gives us hope.
It now says its purpose is to “unlock the power of food to enhance quality of life for everyone, today and for generations to come”.
Companies require profits to survive. But if profit and making chocolate are their only drivers, they are likely to hurt people and the environment while doing it.
This Easter it is possible to support firms that are making profits without hurting the planet or its inhabitants. Our scorecard finds there are more and more of them.![]()
John Dumay is a professor in the department of accounting and corporate governance at Macquarie University. Cristiana Bernardi is a senior lecturer in accounting and financial management at The Open University; Samuel Mawutor is a PhD student in geography and geospatial sciences at Oregon State University, and Stephanie Perkiss is an associate professor at University of Wollongong.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.



COMMENTS
SmartCompany is committed to hosting lively discussions. Help us keep the conversation useful, interesting and welcoming. We aim to publish comments quickly in the interest of promoting robust conversation, but we’re a small team and we deploy filters to protect against legal risk. Occasionally your comment may be held up while it is being reviewed, but we’re working as fast as we can to keep the conversation rolling.
The SmartCompany comment section is members-only content. Please subscribe to leave a comment.
The SmartCompany comment section is members-only content. Please login to leave a comment.